The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located on the front of your neck, right below the Adam’s apple. This gland is in charge of producing different types of hormones. These hormones play an important role in many different processes around the body, including metabolism, growth, development, body temperature, and energy.
As a result of its multifunctional nature, for such a small gland, the thyroid does have a number of diseases associated with it.
Women are five to eight more times likely to have thyroid problems. Studies show that one in eight women will develop a thyroid issue during her lifetime.
These thyroid diseases are broadly classified as Hypothyroidism (low levels of thyroid hormone) and Hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormone in the body)
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, also known as underactive thyroid disease, is a condition in which your thyroid isn’t producing the thyroid hormones in sufficient quantity. As mentioned earlier, thyroid hormones help regulate your body’s temperature, metabolism amongst other things. When you have reduced levels of these hormones, many processes in the body are slowed down significantly. Many of the symptoms may be vague and nonspecific, but when considered altogether should point to a possible diagnosis of hypothyroidism.
That said, here are the most commons symptoms of hypothyroidism:
● Weight gain
● Cold intolerance
● Menstrual cycle changes
● Fatigue
● Dry brittle hair and hair loss
● Depression
● Muscle weakness and slow reflexes
● Memory problems
● Slow heartbeat
As mentioned above, some of these symptoms are quite common, and the only way to confirm a diagnosis of hypothyroidism is by taking a blood test.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, which is also known as overactive thyroid, is the opposite of hypothyroidism. In patients with hyperthyroidism, the gland is producing excess amounts of thyroid hormones. Way more than the body needs. This hormone excess speeds up many processes in the body. This can lead to increased metabolism, weight loss and a rapid heart beat.
When you have hyperthyroidism, your body’s metabolism is faster than usual and ultimately causes rapid weight loss and a faster heartbeat.
One of the causes of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease, which is an autoimmune disorder where some disordered processes affecting your immune system, causes your thyroid to produce more hormones than usual, making it overactive.
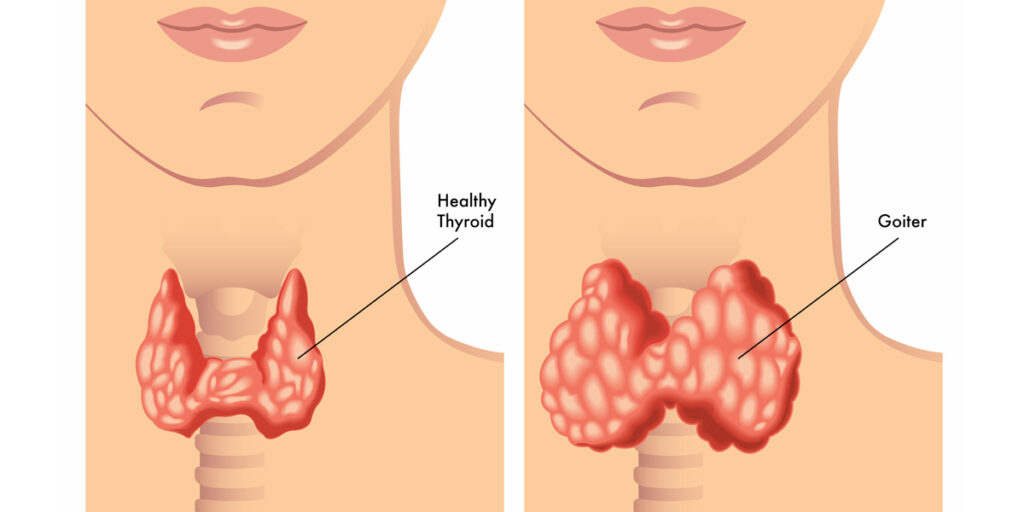
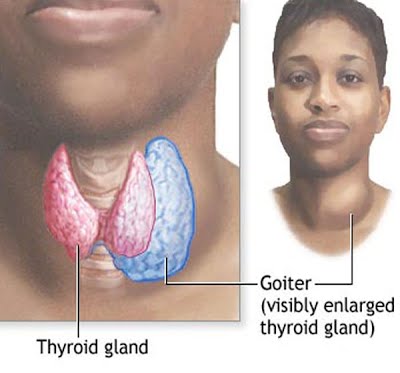
Another possible presentation of hyperthyroidism is goiter, which is a condition in which your thyroid gland grows larger.
The symptoms of hyperthyroidism are the reverse of hypothyroidism while they share some common symptoms as follows:
● Weight loss
● Heat intolerance
● Rapid heartbeat
● Sweating
● Menstrual cycle changes
● Nervousness, anxiety, and irritability
● Fatigue and muscle weakness
● Thyroid enlargement
● increased appetite
● Tremors
As with hypothyroidism, a blood test and some physical tests can help determine if you have hyperthyroidism.
What Do You Need to Do If You Have These Symptoms?
All of these symptoms are your body’s way of telling you something isn’t right. Even if you don’t have any thyroid problems, these symptoms need to be investigated as soon as you notice them.
Untreated thyroid issues can lead to many complications across various organs in the body, including the heart, bones, and muscles. If you’re a woman, you can also experience problems with your fertility, and if you’re pregnant, your baby might be born with health issues as well.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, you should go to your doctor as soon as possible to determine the cause of these problems and find a possible solution.
Following blood tests and physical examination, if you are diagnosed with a thyroid problem, treatment can usually be commenced immediately.
There are not many things you can do to prevent thyroid problems but the good news is that most thyroid problems can be treated medically and in some cases, surgically.