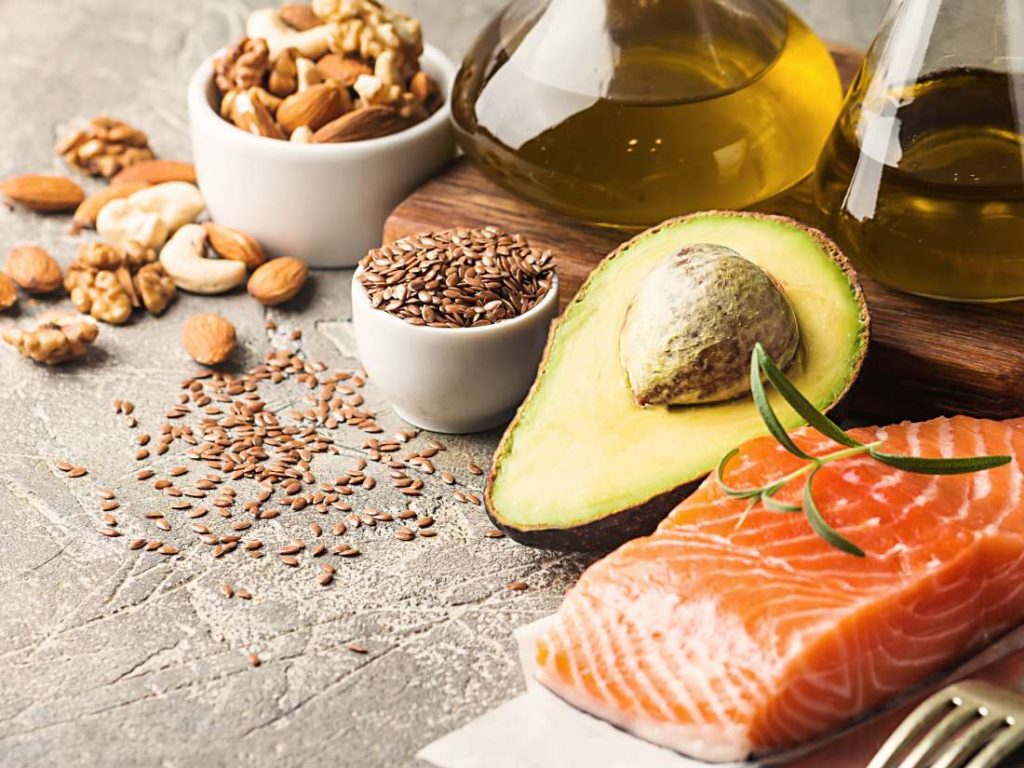
Fat is one of the three essential macronutrients the body needs, along with carbohydrates and protein. However, many people tend to avoid fats because the assumption is that if you consume fats then you will end up….fat. But this isn’t exactly correct. Some fats are healthy while some are not and healthy fats are also an important part of a balanced diet.
Understanding healthful vs. unhealthful fats
Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are healthful fats that might:
- benefit the heart
- lower LDL cholesterol
- improve insulin levels
- improve blood glucose levels
- fight inflammation.
The two most well-known PUFAs are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These are essential fats that people must get from the food they eat because the body is unable to make them. Studies have linked omega-3 fats to many health benefits, especially the prevention of heart disease and stroke. Some of the best sources of these fatty acids include avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
As a general guide, healthful fats — such as olive oil — are liquid at room temperature.
Saturated fats and trans fats, on the other hand, are considered unhealthful fats. Foods rich in these substances, such and butter and lard, are often solid at room temperature.
Older research reported that saturated fat had a negative impact on cholesterol levels and heart health, but newer studies suggest it is not as bad as once thought. However, most health organizations still recommend limiting saturated fat in the diet and replacing them with MUFAs and PUFAs.
Trans fats
Always avoid trans fats. Artificial trans fats, listed on labels as partially hydrogenated oils, are extremely unhealthful even in small quantities. They trigger inflammation that may increase the risk of:
- heart disease
- stroke
- diabetes
- many other health conditions.
The following foods contain trans fats:
- fried foods
- frozen foods, such as pizzas and pies
- baked goods
- Margarine

Keep reading to discover some of the benefits of healthy fats in your body.
Lowered Cholesterol
In the past, scientists opined that removing fat from your diet would result in lowered cholesterol levels. More recently, scientists have come to realize that healthy fats may actually help lower levels of “bad” cholesterol in the bloodstream. Studies recommend incorporating eating fatty fish such as mackerel, salmon, trout, and herring to your diet in order to prevent raised cholesterol levels. Avoid frying your fish, fried foods are often cooked in hydrogenated oils, which are high in trans fats and they’re not good for you. Trans fats raise bad (LDL) cholesterol levels, lower good (HDL) cholesterol levels, and raise your chance of having heart disease. Instead, choose to bake, broil, or grill your fish.
Improved Heart Health
Studies have shown that eating one to two servings of fish each week could prevent a heart attack. Fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, and herring are rich in the omega-3 fatty acids that have heart-protective benefits. Other types of fish, such as cod, crab, oysters, trout, and shrimp, can be healthy choices.
Nutrient Absorption
A diet that includes healthy fats will help your body absorb certain nutrients. The absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K is improved by dietary fats. Therefore, including a dash of olive oil on your salad may improve the absorption of the vitamins in your veggies and leafy greens.
Improved Skin Health
Your skin can also benefit from the inclusion of healthy fats in your diet. The unsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, and fatty fish can help plump up your skin and decrease the appearance of wrinkles. Omega-3 fatty acids found in these foods also fight the inflammation that contributes to saggy, red, or acne-riddled skin. Including antioxidant-rich berries and citrus fruits in your diet will also help improve the appearance of your skin. The vitamin C in these foods may aid in the synthesis of collagen, keeping your skin strong and supple.
Decreased Inflammation
Inflammation plays a role in many disease processes of the body. An anti-inflammatory diet includes foods such as tomatoes, olive oil, green leafy veggies, nuts, fatty fish, fruits, and berries. To fight inflammation, minimise or avoid consuming inflammatory foods such as goods made from refined white flour, fried foods, fast food, soda, red meats, and liquid margarine.
Improved Brain Health
The omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon, herring, and tuna provide your brain with the fats needed for proper function. Furthermore, the omega-6 fatty acids in nuts and seeds may also offer brain protection. Some studies report that polyunsaturated fats may help prevent age-related decline in mental functions such as thinking, understanding, learning, and memory.
Hopefully you realise now that fats can be good, you have to choose wisely and as with everything else, moderation is key because when consumed in excessive quantities, you may lose the benefits provided by these healthy fats.