Hormonal methods of birth control are those methods that use synthetic hormones mimicing those naturally produced by the female body to prevent pregnancy by interfering with ovulation, fertilization, and/or implantation of the fertilized egg. They are reversible methods and do not interfere with sex but they do not offer any protection from sexually transmitted diseases.
The two hormones most commonly involved are estrogen and progestin and together they work by stopping the release of eggs from the ovaries and causing changes in the lining of the fallopian tubes, cervix and uterus which prevent the sperm from joining with an egg and also make the lining unfavourable for implantation.
Hormonal methods of contraception should only be prescribed by a doctor after proper consultation and assessment based on detailed family history and current medical conditions amongst other considerations.
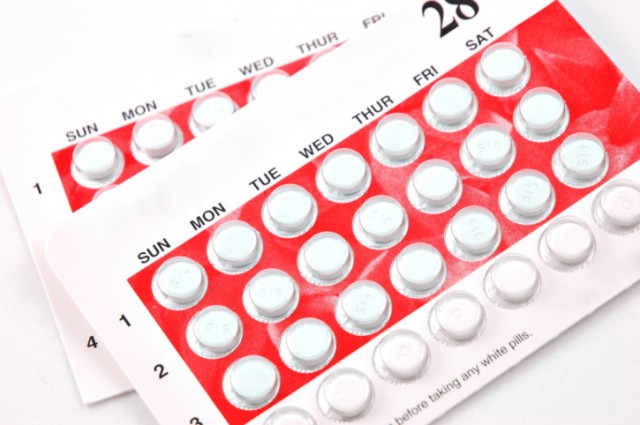
Oral contraceptives
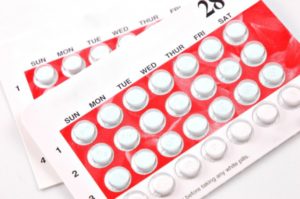 Combined oral contraceptives
Combined oral contraceptives
This is the most common hormonal method. It uses two Synthetic hormones (progesterone and/or estrogen) like those produced by the body to regulate the menstrual cycle They are available as a pack of 21 or 28 day tablets. It is essential to take the pill around the same time every day for optimal effectiveness. Setting an alarm on your phone should help with this. If you miss a pill (or start a pack of pills too late), you may need to use an additional form of birth control.
Your doctor may advise you not to take the combined pill if you:
● Are older than 35 and smoke
● Have a history of blood clots
● Have a personal/ family history of breast, liver, or endometrial cancer
Progestin only pill (also known as the mini pill)
The progestin-only pill is different from combined oral contraceptives in that it contains only one hormone, called progesterone. They also work by thickening cervical mucus, decreasing the release of eggs or fertilization and changing the lining of the fallopian tubes and uterus. Irregular bleeding is common side effect with the mini pill.
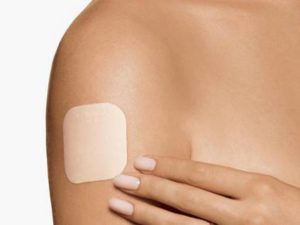
The Patch
Also called by its brand name, Ortho Evra, this skin patch is placed directly on the skin. It contains the hormones estrogen and progestin which are released from the patch directly through the skin into the bloodstream. It can be worn on the lower abdomen, buttocks, outer arm, or upper body. A new patch is worn once a week for 3 weeks. No patch is worn in the fourth week in order to have a period.
The patch is less effective in women weighting more than 90kg.
Shot/injection
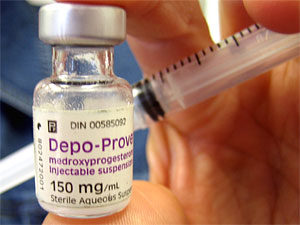 The birth control injection is often called by its brand name Depo-Provera. Injections of the hormone progestin are given in the buttocks or arm every 3 months. It is an excellent alternative for women 35 and older who smoke.
The birth control injection is often called by its brand name Depo-Provera. Injections of the hormone progestin are given in the buttocks or arm every 3 months. It is an excellent alternative for women 35 and older who smoke.
The shot should not be used more than 2 years in a row because it can cause a temporary loss of bone density which increases the longer this method is used. The bone does start to grow after this method is stopped. But it may increase the risk of fracture and osteoporosis if used for a long time. It is important to note that Depo provera may stop menses or make them very light.
Also It may delay your chances of getting pregnant after the shots are stopped. It can take between six and eighteen months for menstruation and ovulation to return consistently.
Vaginal ring
 This is commonly called by it’s brand name, NuvaRing. It is a thin, flexible ring that contains synthetic low dose hormones progestin and estrogen. It is placed directly into the vagina where hormones are released from the ring and are directly absorbed through the walls of the vagina then distributed into the bloodstream.
This is commonly called by it’s brand name, NuvaRing. It is a thin, flexible ring that contains synthetic low dose hormones progestin and estrogen. It is placed directly into the vagina where hormones are released from the ring and are directly absorbed through the walls of the vagina then distributed into the bloodstream.
The ring is worn for 3 weeks, taken out for the week that you have your period, and then a new ring should be put in afterward.
If the ring is kept out of the vagina longer than 3 hours on any day during the 21 day period (3weeks) pregnancy can occur; therefore a back-up method (condoms) is recommended for 7 days.
Hormonal methods of birth control produce a wide variety of side effects ranging from changes in your period, mood changes, abdominal disturbances, weight gain amongst others which should be explained to you by your doctor/health care provider. If any side effects hinder you from using your chosen method optimally then you may need to visit your health care provider again to discuss other options.
Many of the public hospitals in Nigeria (i’m sure of Lagos at least) offer a good number of the items listed above such as the Depo provera, oral contraceptive pills, shots and intra uterine devices and are usually offered almost free of charge. So feel free to walk into your neighbourhood primary health care centre to find out what may be available for you.