We have previously discussed sickle cell on this platform in this post where were looked into the myths vs the facts surrounding sickle cell.
Today we’ll be looking at a few of the major complications that can occur as a result of sickle cell disease. The most common symptom/complication which many people are aware of is the painful crisis which people with sickle cell suffer. However, there are several other complications of this disease.
Severe or long-lasting anemia can damage the heart, brain, lungs, kidney, spleen, and other organs of the body. Very severe anemia may even cause death.
Some of these complications include:
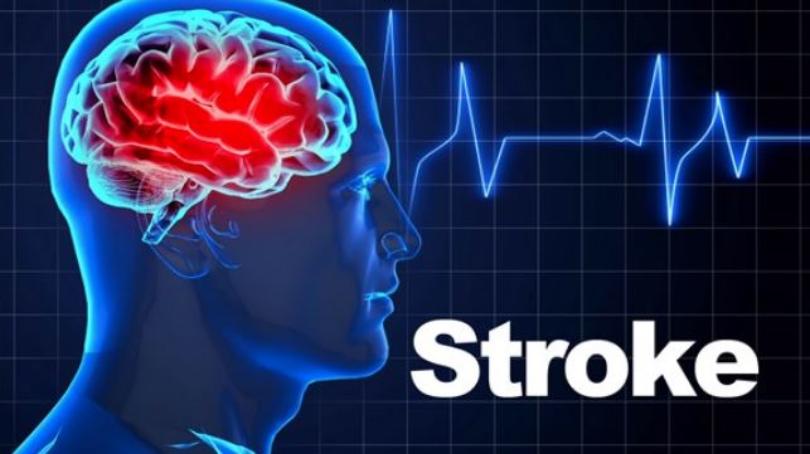
Stroke
Stroke is usually associated with older people, especially those with hypertension, however it can also be seen in young people. SCD is the leading cause of stroke in children. A stroke can occur if sickle cells block blood flow to an area of the brain. Symptoms of stroke include paralysis or weakness on one side of the body especially in the face, arms and legs, seizures, confusion, trouble walking or talking (slurred speech), numbness and a severe headache and loss of consciousness. It is important to seek medical help immediately any of these symptoms is noticed. A stroke can be fatal.
Organ damage
In patients with SCD, the red blood cells take an abnormal sickle shape. These sickle cells can block blood flow through blood vessels and this can deprive the affected organ of blood and oxygen. In sickle cell anemia, blood is also chronically low on oxygen. Chronic deprivation of oxygen-rich blood can damage nerves and organs in the body, including the kidneys, liver and spleen. Organ damage can be fatal.
Blindness
Sickle cells can block tiny blood vessels that supply the eyes. Over time, this can damage the portion of the eye that processes visual images (retina) and lead to blindness.

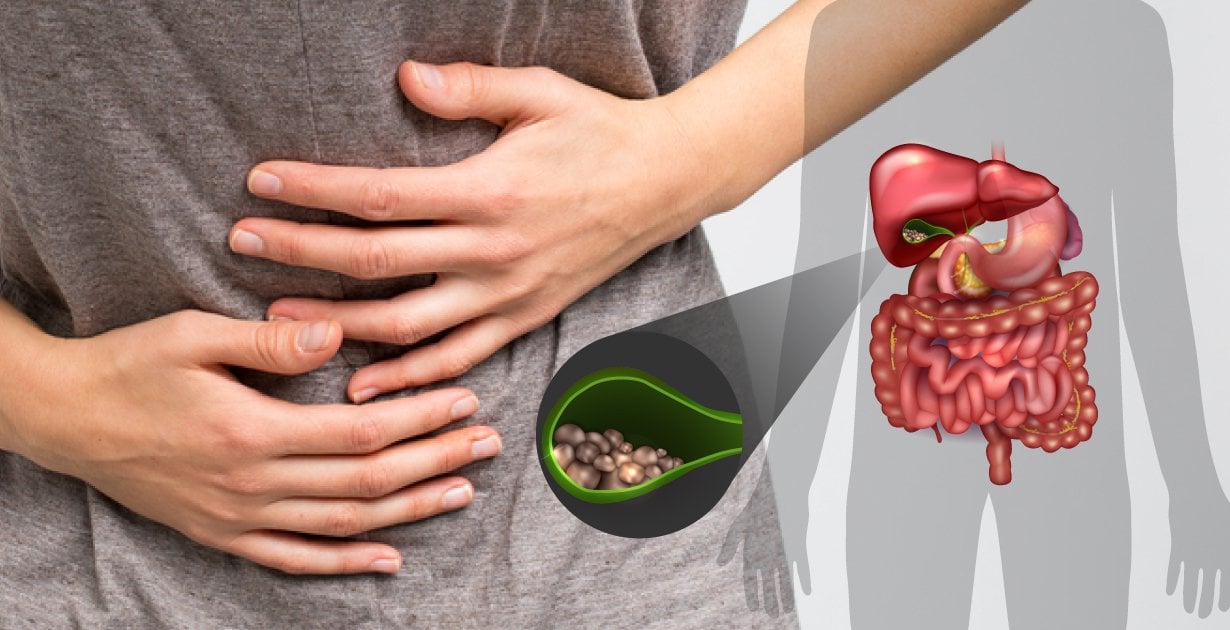
Gallstones
The breakdown of red blood cells produces a substance called bilirubin. This substance can also cause yellowing of the skin and eyes commonly known as jaundice. A high level of bilirubin in your body can lead to gallstones. This can cause chronic jaundice as well as pain and may ultimately lead to removal of the gallbladder.
Priapism
Men with sickle cell anemia can have painful, long-lasting erections, a condition called priapism. As occurs in other parts of the body, sickle cells can block the blood vessels in the penis. This can damage the penis and lead to impotence.
Splenic sequestration crisis
The spleen is located in the upper left side of the belly, it is an organ that filters germs in the blood, breaks up blood cells, and makes a kind of white blood cell. A splenic sequestration crisis occurs when red blood cells get stuck in the spleen, making it enlarge quickly. This type of crisis occurs most often in young children between 10 and 27 months of age.
Symptoms include sudden weakness, pale lips, fast breathing, extreme thirst, abdominal (belly) pain on the left side of body, and fast heartbeat.
Parents of a child with SCD should learn how to feel and measure the size of their child’s spleen and seek help if the spleen is enlarged.
Pulmonary hypertension
People with sickle cell anemia can develop high blood pressure in their lungs (pulmonary hypertension). This complication usually affects adults rather than children. Shortness of breath and fatigue are common symptoms of this condition, which can be fatal.
Preventing Complications
Many times these complications can be prevented with proper care and constant monitoring of people with SCD.
Blood transfusions are commonly used to treat worsening anemia and sickle cell complications. Most patients with sickle cell disease have at least occasional blood transfusions. Patients with severe complications–such as stroke and acute chest syndrome–may require months or years of regular transfusions every three to four weeks to prevent ongoing damage.
Hydroxyurea treatment may be helpful in reducing crises and the need for transfusions.
People with sickle cell disease should have regular checkups to detect eye damage. And a simple ultrasound test of the head can identify children at high risk for strokes.