As the world marks another World Tobacco Day on the 31st of May 2018, it’s as good a time as ever to remind everyone of the negative effects of tobacco on your body and health. No matter how you smoke it, tobacco is dangerous to your health. There are no safe substances in any tobacco products, from acetone (chemical found in nail polish) and tar to nicotine and carbon monoxide. These substances when inhaled don’t just affect your lungs. They can affect your entire body.
Smoking can lead to a variety of ongoing complications in the body, as well as long-term effects on your body systems.
These effects are too numerous to list in one post, however here are a few to think about, starting from head to toe.
Brain
Nicotine from cigarettes is a very addictive substance. Nicotine addiction is hard to overcome because it changes your brain. The brain develops extra nicotine receptors to accommodate the large doses of nicotine from tobacco. When the brain stops getting the nicotine it’s used to, the result is nicotine withdrawal. This is why smokers feel anxious, irritable, and have strong cravings for nicotine when they haven’t had a cigarette.

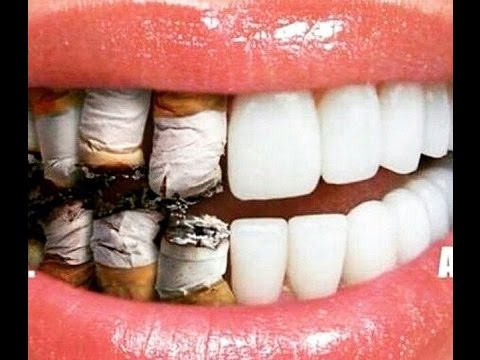
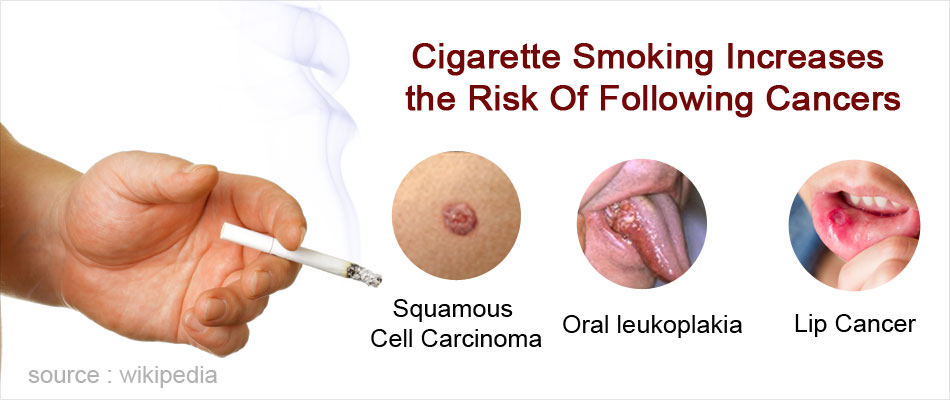
Mouth
Smoking takes a toll on your mouth. Smokers have more oral health problems than non-smokers, like mouth sores, ulcers and gum disease. Smokers are more likely to have cavities and lose their teeth at a younger age. They are also more likely to get cancers of the mouth and throat.
Face
Smoking can cause your skin to be dry and lose elasticity, leading to wrinkles. Many smokers start to have wrinkles in their early 30s. Wrinkles can begin to appear around the mouth and eyes, adding years to a smokers face.
Heart problems
Smoking raises your blood pressure and puts stress on your heart. Over time, stress on the heart can weaken it, making it less able to pump blood to other parts of your body. Carbon monoxide from inhaled cigarette smoke also contributes to a lack of oxygen, making the heart work even harder. This increases the risk of heart disease, including heart attacks.

Blood clots
Smoking makes your blood thick and sticky. The stickier the blood, the harder your heart must work to move it around your body. Sticky blood is also more likely to form blood clots that block blood flow to your heart, brain, and legs. Over time, thick, sticky blood damages the delicate lining of your blood vessels. This damage can increase your risk for a heart attack or stroke.
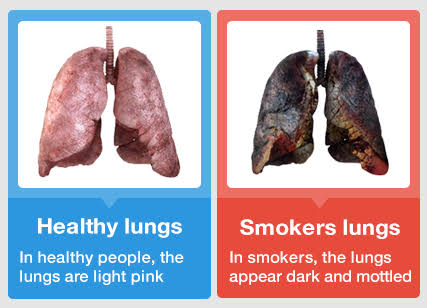
Lung problems
Smoking causes inflammation in the small airways and tissues of your lungs. This can cause feelings of chest tightness, shortness of breath and wheezing. Continued inflammation can lead to formation of scar tissue, which leads to physical changes to your lungs and airways that can make breathing hard. Years of lung irritation can give you a chronic cough with mucus.
Smoking also destroys the structures responsible for clearing your air passage, for this reason, smokers get more colds and respiratory infections than non-smokers.
Generally smoking has a major dangerous effect on the lungs and greatly increases the risk of chronic non reversible lung conditions such as emphysema, chronic bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and even cancer.
Cancer
Your body is made up of cells that contain genetic material, or DNA, that acts as an “instruction manual” for cell growth and function. Every single puff of a cigarette causes damages to your DNA. When DNA is damaged, the “instruction manual” gets messed up, and the cell can begin growing out of control and create a cancer tumor. The body tries to repair the damage that smoking does to DNA, but over time, smoking can wear down this repair system and lead to cancer (like lung cancer).
Sexuality and reproductive system
Nicotine affects blood flow to the genital areas of both men and women. For men, this can decrease sexual performance. For women, this can result in sexual dissatisfaction by decreasing lubrication and the ability to reach orgasm. Smoking may also lower sex hormone levels in both men and women. This can possibly lead to decreased sexual desire. Toxins from cigarette smoke can also damage the genetic material in sperm, which can cause infertility or genetic defects in children born to smokers.

More Broken Bones
Ingredients in cigarette smoke disrupt the natural cycle of bone formation. Therefore the body is less able to form healthy new bone tissue, and it breaks down existing bone tissue more rapidly. Over time, smoking leads to a thinning of bone tissue and loss of bone density. This causes bones to become weak and brittle. Compared to non-smokers, smokers have a higher risk of bone fractures, and their broken bones take longer to heal.
These are only a few of the effects of smoking and clearly none of them is a positive effect. If you do not smoke, you’re doing well and your body is certainly grateful for it. If you do smoke however you may wish to consider stopping in order to prevent some of these long term effects.
Quitting smoking can be difficult but is achievable with the right support. Speak to your doctor to get help to quit this harmful habit.