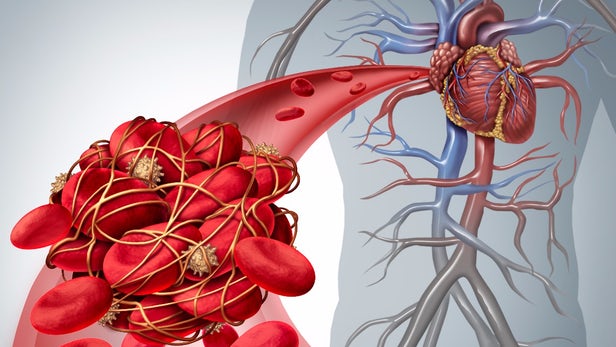
The human body is designed with some inbuilt protective mechanisms. One of such mechanisms is the formation of blood clots. When there is a cut or an injury, this triggers a series of reaction in the body to form a clot in order to prevent excessive blood loss.
Unfortunately these blood clots can also cause problems when they cause blockages where we do not need them, like inside the blood vessels and circulatory system. So imagine that the blood vessels are tiny pipes through which blood flows around the body to supply all the different organs so if a blockage occurs they can lead to heart attacks, strokes, or other serious complications that can prove life-threatening.
Dangers of Clots
Blood clots can cause blockages in different locations, each of which requires emergency medical treatment. Heart attacks may occur when clots block blood flow to the heart, while a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) refers to clots in the legs. These may break off and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism, which can prove life-threatening. The same is true of strokes, which is when clots block blood flow to the brain. A lack of blood means a lack of oxygen, and therefore tissue death.
Any of thee conditions could prove fatal, therefore it is important to be informed about them and take steps to prevent and treat them when we can.

Risk Factors
As with many other ailments, the chances of having a problematic clot vary depending on other factors. While we cannot always alter these factors, it is still wise to be aware of them, so that we can better monitor our health and reduce the risk of tragedy. Here are some factors that may increase your risk of developing a blood clot. If these any of these apply to you, consider making lifestyle changes to improve your overall health.

Obesity
Being overweight can increase the chances of having blood clots form. This is a risk that only increases more and more, depending on how much body weight one carries around. This is as a result of the excess cholesterol that builds up within the blood vessels, which may stick together, causing the vessels to get narrower and narrower, making it difficult for blood to pass through freely. Obesity may also compound with other factors that increase the risk of blood clots.
Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle also contributes to blood clots in inappropriate places. When one considers that obesity is generally associated with a less active lifestyle, it becomes clear how these two elements might compound to drastically increase the odds of a problematic clot. However, obesity is not the only factor when it comes to being sedentary; unfortunately, those who are injured and require large amounts of bed rest are at an increased risk for such clots as well.
Smoking
There are a lot of health risks associated with smoking, and blood clots are another to add to the list. This is because of the effect that smoking has on the circulatory system. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can cause damage to the arteries, which leads them to harden. Cigarette smoke can also generate plague. This can lead to a whole host of heart-related conditions, like high blood pressure, but also including blood clots, which increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and pulmonary embolisms. For smokers, there is a lot more at stake than just one’s respiratory health.
Serious Illness
While hospital stays from various injuries can lead to blood clots, even illnesses that don’t leave you bedridden can result in an increased risk. For example, there are certain types of cancer that fall into this category. Other illnesses include inflammatory bowel diseases, HIV, or even diabetes. In addition to their other symptoms, these diseases may cause blood clotting, so it may be wise to get tested for clots for those who have such conditions. Serious physical injuries may also result in blood clots in unusual spots; be sure to discuss such things with a medical professional.
Family History
If there is a history in your family of blood clots, you will have an increased risk of developing them yourself. Genetics are powerful, and unlike other factors, there’s nothing we can do about what we inherit. Generally, blood clots occur in situations where the blood is thicker. With that knowledge in mind, if there is a family history of blood clots, it is worth the time to discover if a disorder is the culprit behind thicker blood, and therefore an increased likelihood of clotting.
Personal History
if you have a personal history of blood clots, then it’s very possible that you will have them again. This is especially the case if the clots do not result from a particular injury, as many of the other risks for blood clots (Weight, serious illnesses, genetics) are lifelong, or at least chronic conditions. However, it’s not just the presence of risk factors that can lead to recurrent clots. The clots themselves can cause serious damage the veins, which then leads to situations where blood clots are more likely to form.
For those who have already experienced a blood clot, unfortunately, there is about a 33 percent chance that another blood clot will occur within 10 years.
Now that you know just how serious a blood clot can be, you might understand how important it is to prevent them. Many of the risk factors stated above can be modified to reduce risk and as always if you have any concerns be sure to discuss them with your health care professional.